Go to:
GLUCOMETERS
LANCING DEVICES
CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE MONITORING
DEXCOM
MEDTRONIC
FREESTYLE LIBRE

DiabetesSelfManagement: Blood Sugar Monitoring: When to Check and Why
Diatribe.org: Factors Affecting Blood Glucose
What is a Normal Blood Sugar Level?
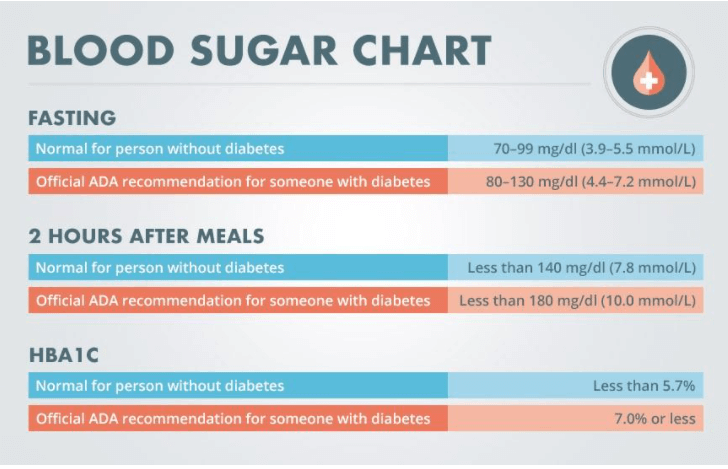 Diabetes Self Management – Blood Sugar Chart
Diabetes Self Management – Blood Sugar Chart
 DiaTribe: Factors that affect glucose levels
DiaTribe: Factors that affect glucose levels
ADA: Safe at School: Blood Glucose Monitoring
Glucose Monitoring Log
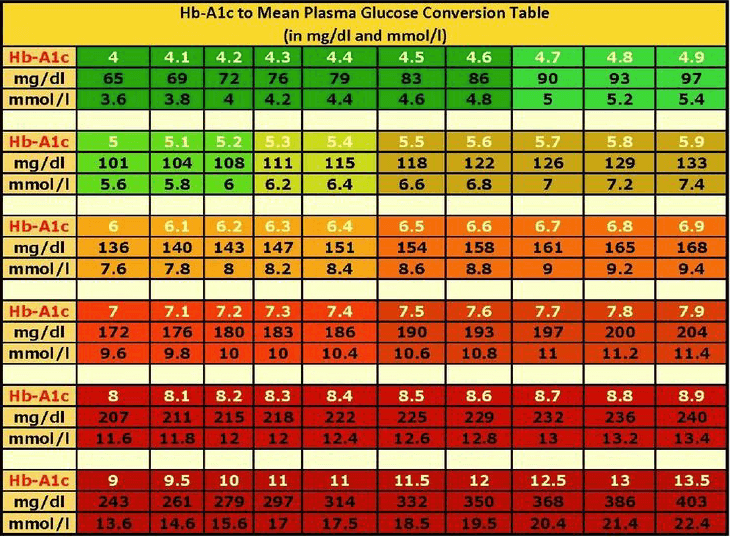 Hb-A1c to Mean Plasma Glucose Conversation Table
Hb-A1c to Mean Plasma Glucose Conversation Table
ADA: A1C/eAG
GLUCOMETERS (click on photo to link to meter information)
LANCING DEVICES
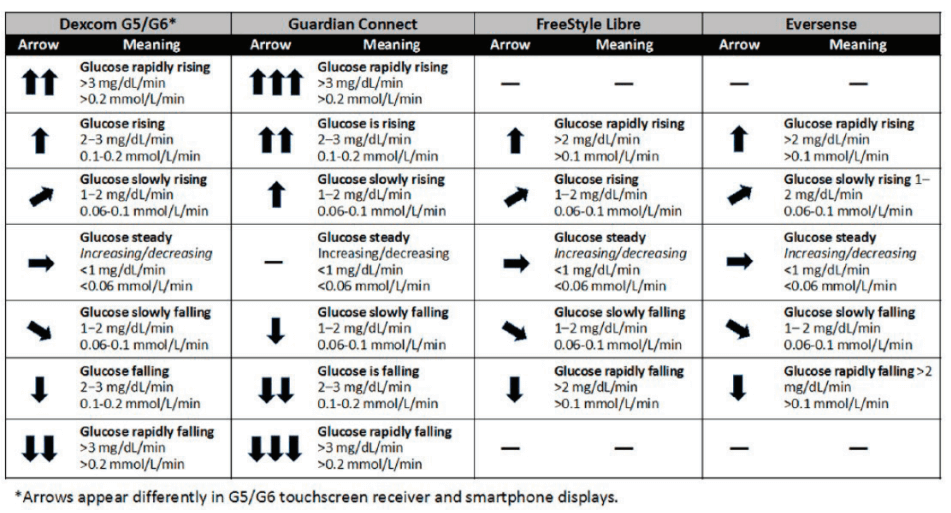
CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE MONITORING
Continuous Glucose Monitoring: The Basics
What is continuous glucose monitoring?
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems use a tiny sensor inserted under the skin to check glucose levels in tissue fluid. The sensor stays in place for several days to a week and then must be replaced. A transmitter sends information about glucose levels via radio waves from the sensor to a pagerlike wireless monitor. The user must check blood samples with a glucose meter to program the devices. Because currently approved CGM devices are not as accurate and reliable as standard blood glucose meters, users should confirm glucose levels with a meter before making a change in treatment.
CGM systems provide glucose measurements as often as once per minute. The measurements are transmitted to a wireless monitor.
CGM systems are more expensive than conventional glucose monitoring, but they may enable better glucose control. CGM devices produced by Abbott, DexCom, and Medtronic have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and are available by prescription. These devices provide real-time measurements of glucose levels, with glucose levels displayed at 5-minute or 1-minute intervals. Users can set alarms to alert them when glucose levels are too low or too high. Special software is available to download data from the devices to a computer for tracking and analysis of patterns and trends, and the systems can display trend graphs on the monitor screen.
Additional CGM devices are being developed and tested. To learn more about such monitors and new products after approval, call the FDA at 1-888-INFO-FDA(463-6332) or at www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/default.htm
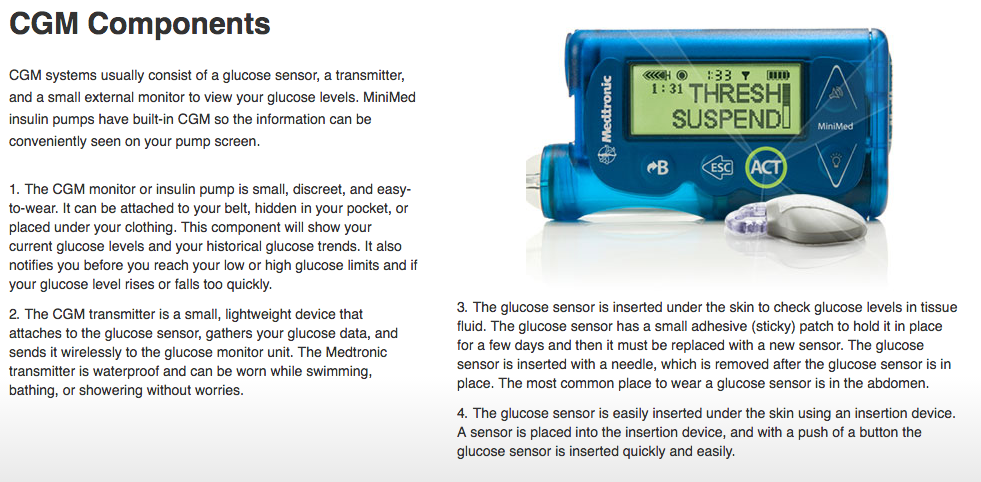
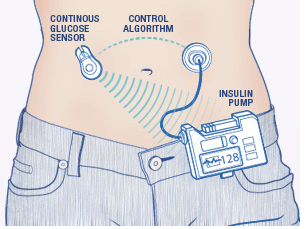 Pump, CGM Sensor and Transmitter
Pump, CGM Sensor and Transmitter
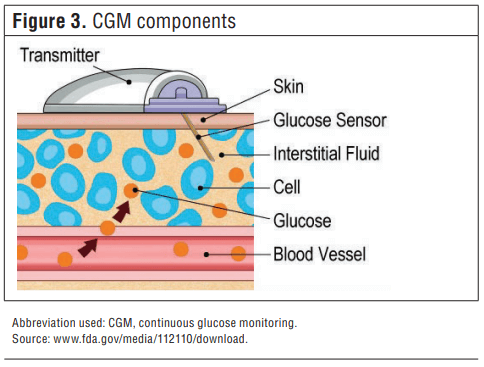 Pharmacy Today: CGM Components
Pharmacy Today: CGM Components
Kruger DF, Edelman SV, Hinnen DA, Parkin CG. Reference guide for integrating CGM into clinical practice. Diabetes Educ. 2019;45 (suppl 1);3S-20S
NIH : Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Diabetes Forecast: Anatomy of a CGM Sensor
Remote Glucose Monitoring in Diabetes Eases Parents’ Fears
What is Continuous Glucose Monitoring?
DEXCOM
G6
G5
DIABETES MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE
G6
Dexcom G6: Start Here
Dexcom G6: Using Your G6
Dexcom G6: User Guide
Dexcom G6: Training Checklist
Keeping the Sensor Patch On
G5
Dexcom G5: Getting Started Guide
Dexcom G5: Your First Week Tutorial
Dexcom G5: School Nurse Guide
DIABETES MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE
Dexcom Clarity – Diabetes Management Software
Dexcom G6: Setting Up Dexcom Share and Follow
Dexcom Share: User Manual
MEDTRONIC
Caring for Your Transmitter and Sensor
Sensors and Transmitters Troubleshooting
Getting Started with the Paradigm Revel CGM (PDF)
Guardian Connect User Guide (PDF)
Getting Started with the Paradigm 522, 722 CGM (PDF)
Getting Started with the CGM for the 530G (PDF)
 VIDEOS
VIDEOS
FREESTYLE LIBRE
FREESTYLE LIBRE 2
FREESTYLE LIBRE 14 DAY
![]()
FREESTYLE LIBRE 2
FreeStyle: Libre 2 User’s Manual
FreeStyle: Libre 2 Setup Overview
FreeStyle Libre 2: Quick Reference Guide
FreeStyle Libre 2: Tips for Kids
FREESTYLE LIBRE 14 DAY
 FreeStyle Libre 14-Day
FreeStyle Libre 14-Day
FreeStyle Libre 14 Day: Setup Overview
FreeStyle Libre 14 Day: User’s Manual
FreeStyle Libre 14 Day: Quick Reference Guide
FreeStyle Libre 14: Sensor Application and Adhesion Guide